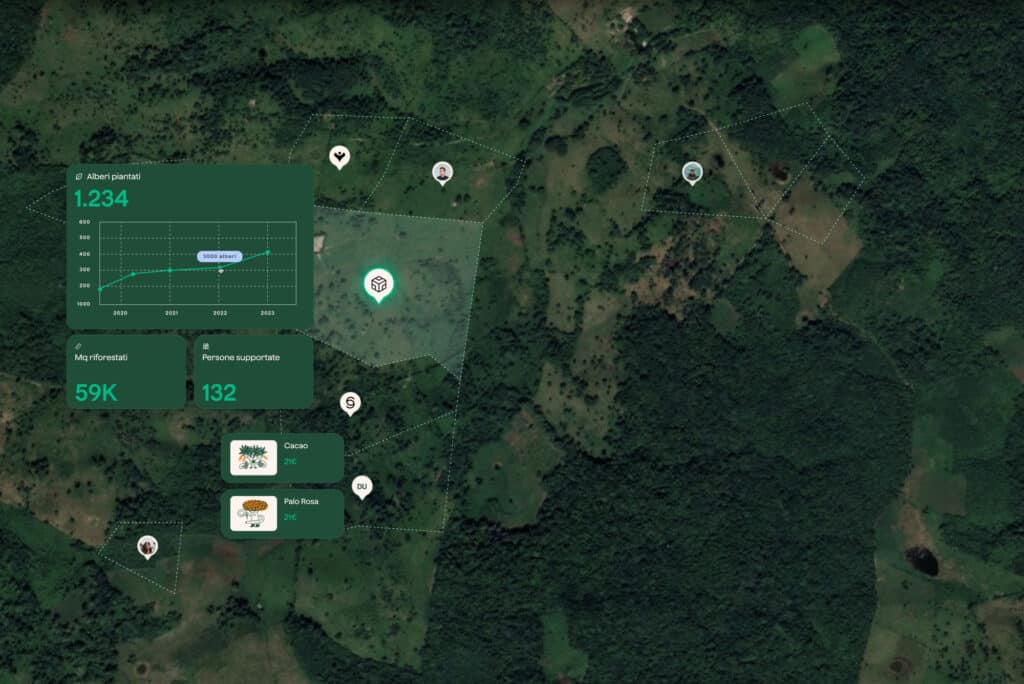
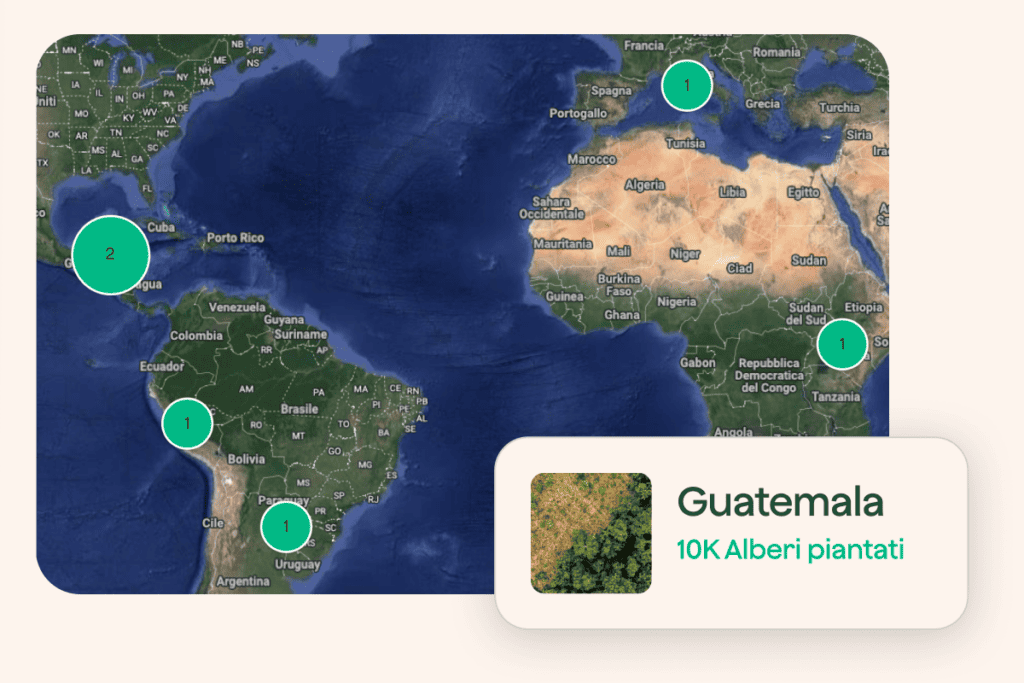
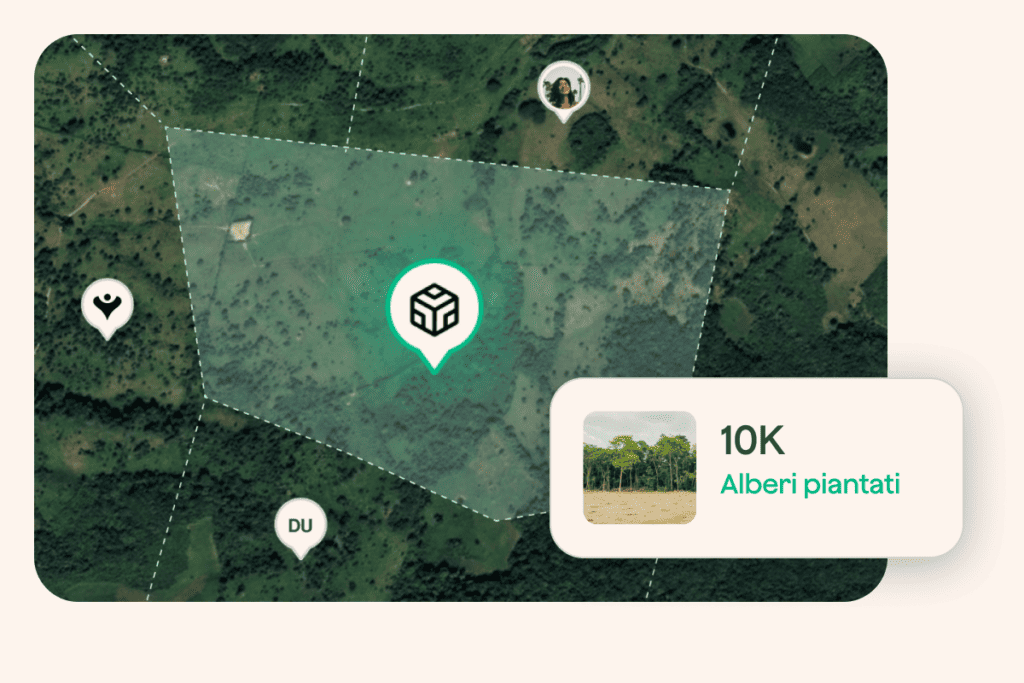
Deforestation consists of completely clearing or removing a significant portion of forest from an area, usually in order to devolve the land to other uses.
A few numbers on deforestation
- Between 1990 and 2020, 420 million hectares of forest were destroyed globally according to the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO);
- During the same period, there was a 10% increase in European forest cover. However, European consumption is responsible for about 10% of global deforestation;
- Agriculture is the main driver of deforestation in all regions of the world. The only exception is Europe, where livestock grazing drives up to 20% of forest destruction.
Read more
Deforestation is caused by a range of human activities that damage both ecosystems and communities. Among these activities, the primary culprit is industrial agriculture. According to the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO), the conversion of forests to cropland accounts for 50 per cent of global deforestation. The two crops most responsible for this destruction are oil palm and soya. This is followed by livestock grazing and, finally, urbanisation, which accounts for only 6% of global deforestation.
Deforestation mainly affects the tropical regions of the world but is driven by the external demand for goods such as palm oil and soya, which are then traded globally.
The destruction of forests does not only translate into the loss of the Earth’s so-called ‘green lungs’ with their incredible capacity to absorb and store CO2 in the atmosphere. Forests are gatekeepers of biodiversity, they protect the soil from erosion, regulate the water cycle and provide important resources for local communities.
Forests are simultaneously threatened by human-induced deforestation and the impacts of climate change, such as fires, droughts and floods. Their destruction in turn accelerates and magnifies the climate imbalance.
Protecting forests is an important action to counter climate change while generating great benefits for people.