Companies
Individuals
Projects
About us
Back
Fight the climate crisis with your business.
Get started
For your business
We offer you concrete, high-impact actions to counter the climate crisis. Find the solution that best fits your business goals.
Browse our services
Back
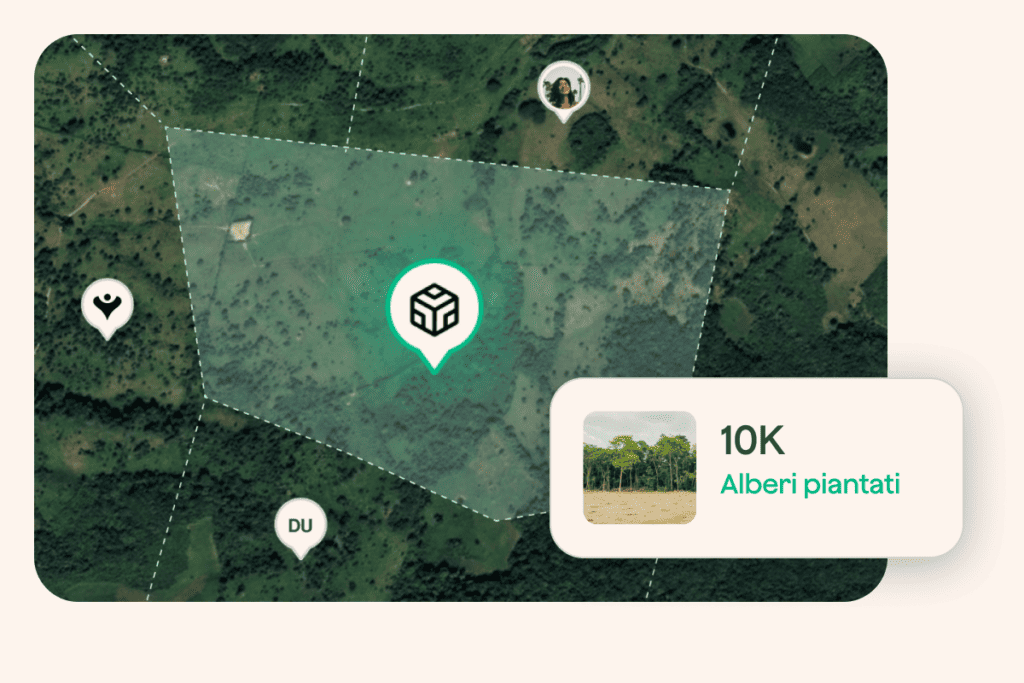
Generate impact, tree after tree.
Get started
Get active for planet Earth.
Countering the climate crisis is the challenge of our century. Become an activist and inspire people around you to act for the future of the planet.
Find out how to do it
Back
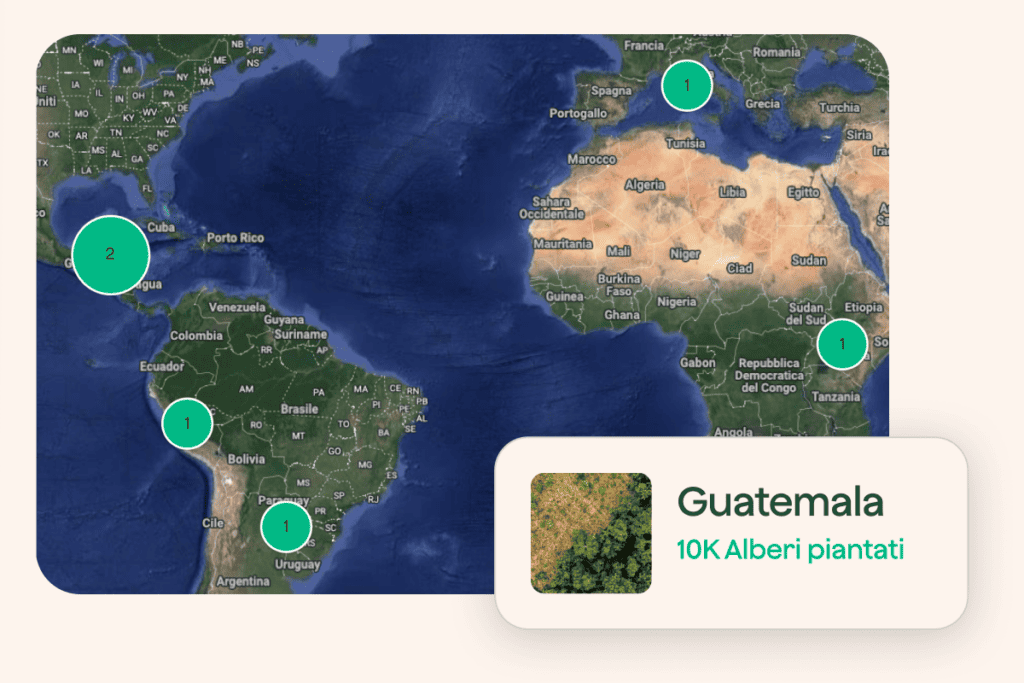
We cultivate resistance all over the world.
Browse our projects
Back
About us
Find out how zeroCO2 was born, discover our milestones and come meet the team.
Read our story
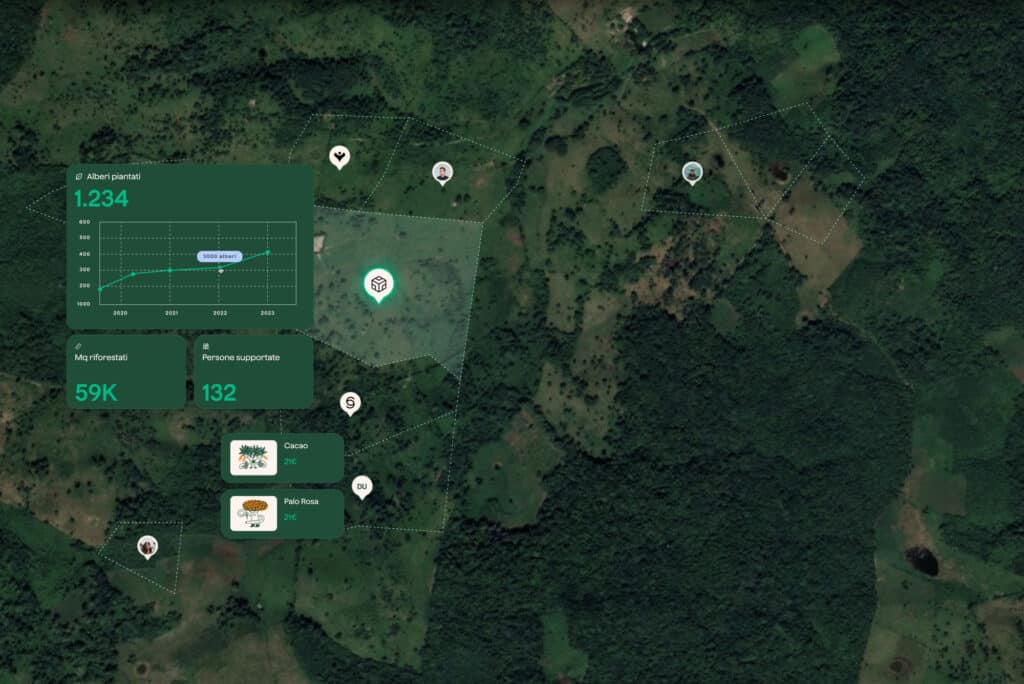
Impact
The goals we want to achieve and those we have already achieved. For people and for the planet.
Discover our impact
Menu
Close